Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is an unpleasant sensation of difficulty breathing that can be temporary or chronic.
This symptom can be caused by a variety of causes, ranging from simple respiratory infections to more serious conditions such as heart failure or asthma.
In this article, we'll explore in depth the origins of dyspnea, its associated symptoms, and solutions to improve your daily breathing.
Understanding Dyspnea: A Feeling of Shortness of Breath
Dyspnea is the medical term used to describe a feeling of **difficulty breathing** or **shortness of breath**.
It may feel like chest tightness, shortness of breath, or difficulty taking a deep breath.
This sensation can appear during **physical exertion**, when lying down or even at rest in the most severe cases.
We generally distinguish two types of dyspnea:
- Acute dyspnea: It occurs suddenly and lasts a short time. It is often linked to a lung infection, an asthma attack, or a pulmonary embolism.
- Chronic dyspnea: It develops gradually and persists over the long term. This type of dyspnea can be due to respiratory (COPD, asthma), cardiac, or neurological diseases.
The main causes of dyspnea
Shortness of breath can be caused by **several factors**, involving the lungs, heart, or other body systems.
Here are the main origins:
- Respiratory problems: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and pulmonary fibrosis are often responsible for shortness of breath.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Heart failure, myocardial infarction, valvulopathy or pulmonary arterial hypertension can limit good blood oxygenation.
- Neurological and muscular causes: Neuromuscular diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, can weaken respiratory muscles and cause difficulty breathing.
- Psychological causes: Anxiety and panic attacks can cause episodes of dyspnea, often accompanied by a feeling of oppression.
- Other causes: Anemia (red blood cell deficiency), obesity, or even certain seasonal allergies can cause a feeling of shortness of breath.
Symptoms of dyspnea
Dyspnea can manifest itself in different ways depending on its cause:
- Difficulty breathing: A feeling of lack of air, as if your lungs are not filling completely.
- Chest tightness: A feeling of weight on the chest that makes breathing difficult.
- Rapid breathing: It may be necessary to breathe faster or more deeply to compensate for the lack of air.
- Wheezing: Asthma and other respiratory conditions can cause wheezing sounds when exhaling.
- Sweating and dizziness: Poor blood oxygenation can lead to general malaise.
- Cyanosis: In severe cases, the skin and lips may take on a bluish tint due to lack of oxygen.
How to relieve and treat dyspnea?
Treatment for dyspnea depends on its cause, but here are some general solutions to relieve shortness of breath and improve your breathing:
- Changing your lifestyle: Avoiding pollution, quitting smoking and engaging in moderate physical activity can limit symptoms.
- Breathing exercises: Diaphragmatic breathing and cardiac coherence improve oxygenation and reduce shortness of breath.
- Medications: Asthma inhalers, bronchodilators, and cardiac diuretics may be prescribed to relieve dyspnea.
- Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, oxygen support may be necessary to maintain good blood oxygen levels.
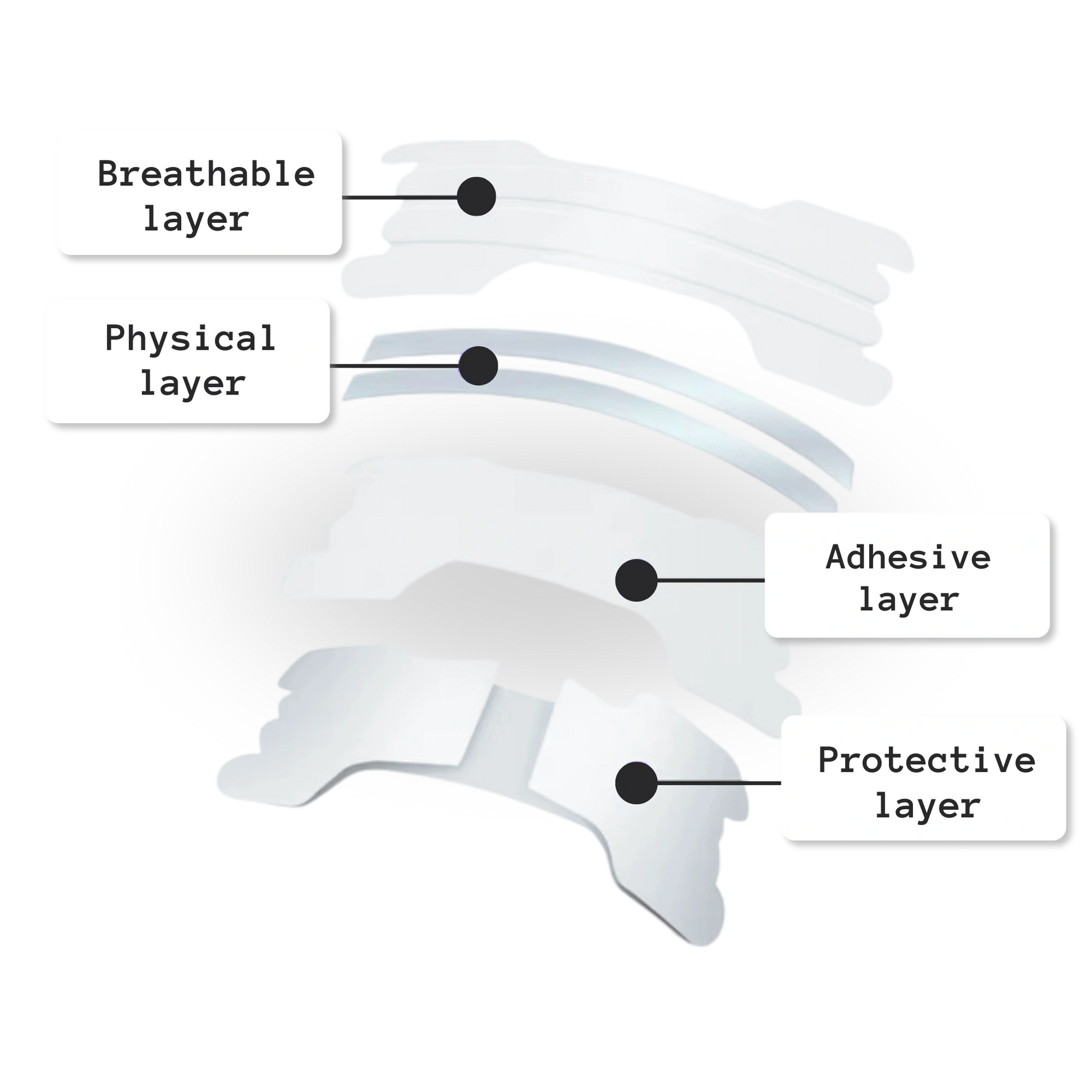
- Use nasal strips: BreatheBetter nasal strips are a natural solution to improve breathing. By widening the nasal passages, they promote smoother airflow, helping to reduce shortness of breath **especially in cases of nasal congestion**.
Dyspnea is a symptom that can reveal a multitude of underlying problems.
By identifying its causes and adopting the right reflexes, it is possible to considerably improve your respiratory comfort.
Do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent shortness of breath.